Products/Services
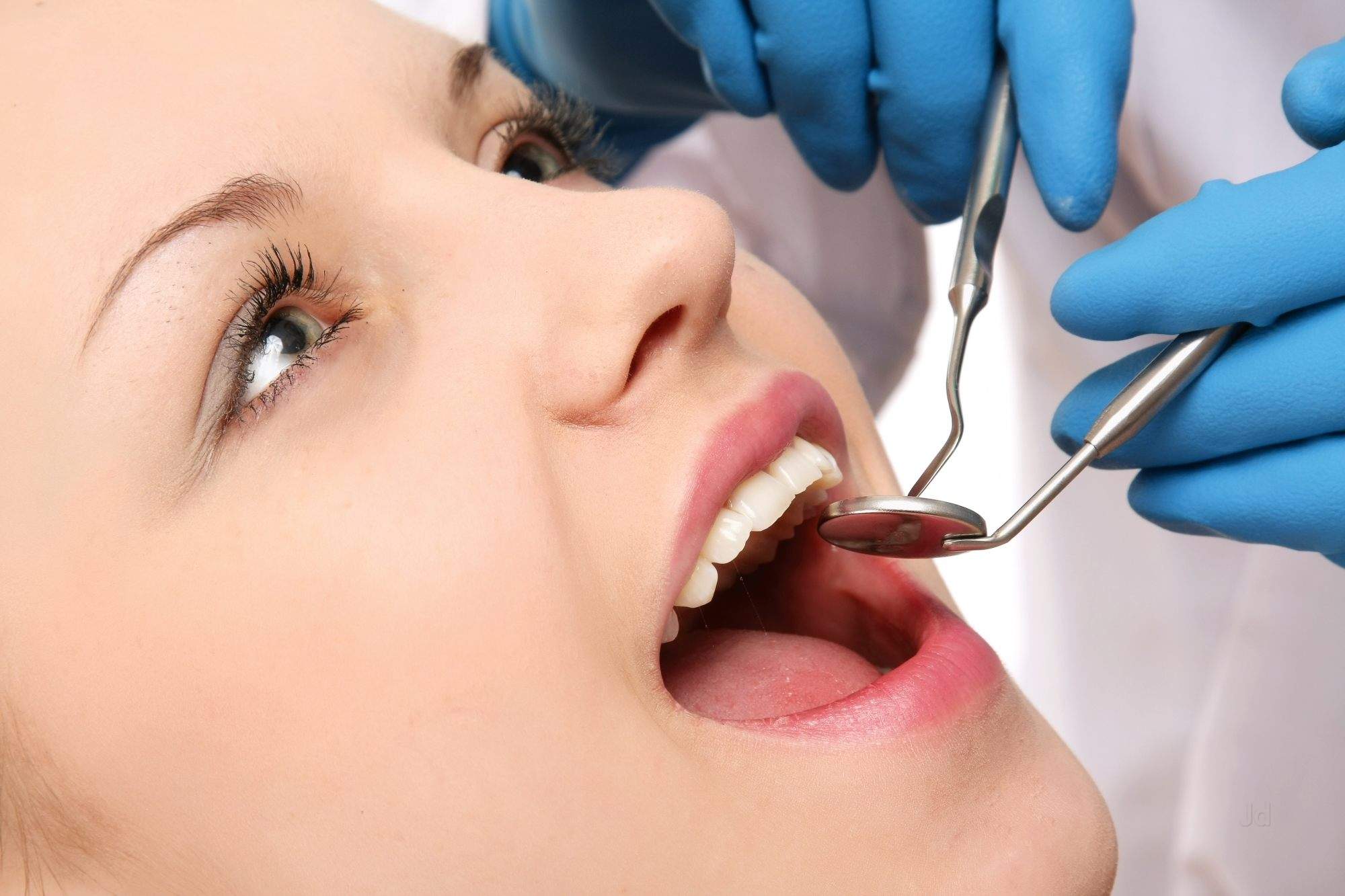
Examination & Diagnosis
An inspection of the teeth and surrounding soft tissues of the oral cavity. The examiner generally uses an explorer, a slender steel instrument with a flexible, sharp point, to probe the minute indentations on tooth surfaces and around dental restorations for signs of demineralization and caries development. Fillings are also inspected, and a radiographic record or imaging of the teeth is usually made. The examiner may also insert a periodontal probe into the soft-tissue sulcus around each tooth to measure the depth of each sulcus and to explore for calculus and root defects. The examination should include inspection of the floor of the mouth, all surfaces of the tongue, the salivary glands and ducts, and the lymph nodes of the neck in order to detect pathology.
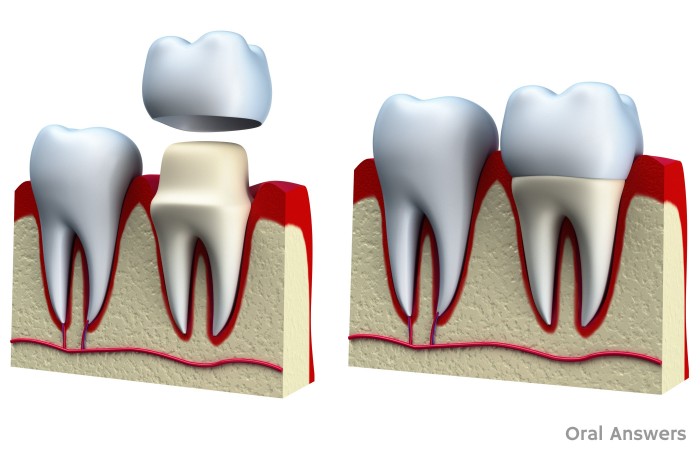
Restorative dentistry
Restorative dentistry encompasses the dental specialties of endodontics, periodontics and prosthodontics and its foundation is based upon how these interact in cases requiring multifaceted care. In addition, restorative needs derive from not only diseases of the teeth like cavities and medical conditions but also from trauma. "Traumatic injuries to anterior(front) teeth are frequently encountered in children and adults". The degree of the trauma will dictate what restorative treatment will be needed and could involve one or more of the dental specialties listed above.
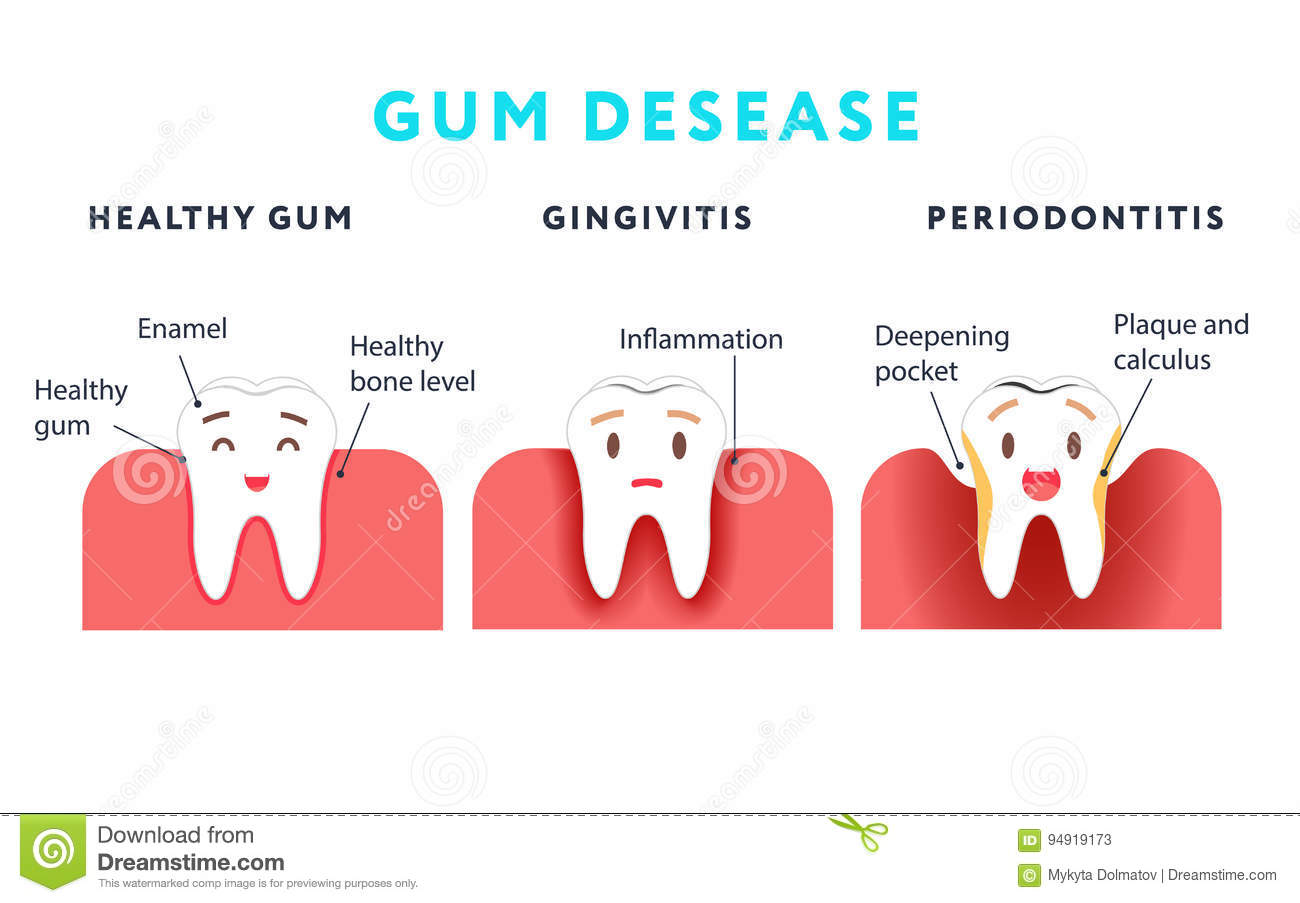
Periodontics
A periodontist is a dentist who specializes in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of periodontal disease, and in the placement of dental implants. Periodontists are also experts in the treatment of oral inflammation. Periodontists receive extensive training in these areas, including three additional years of education beyond dental school. They are familiar with the latest techniques for diagnosing and treating periodontal disease, and are also trained in performing cosmetic periodontal procedures.
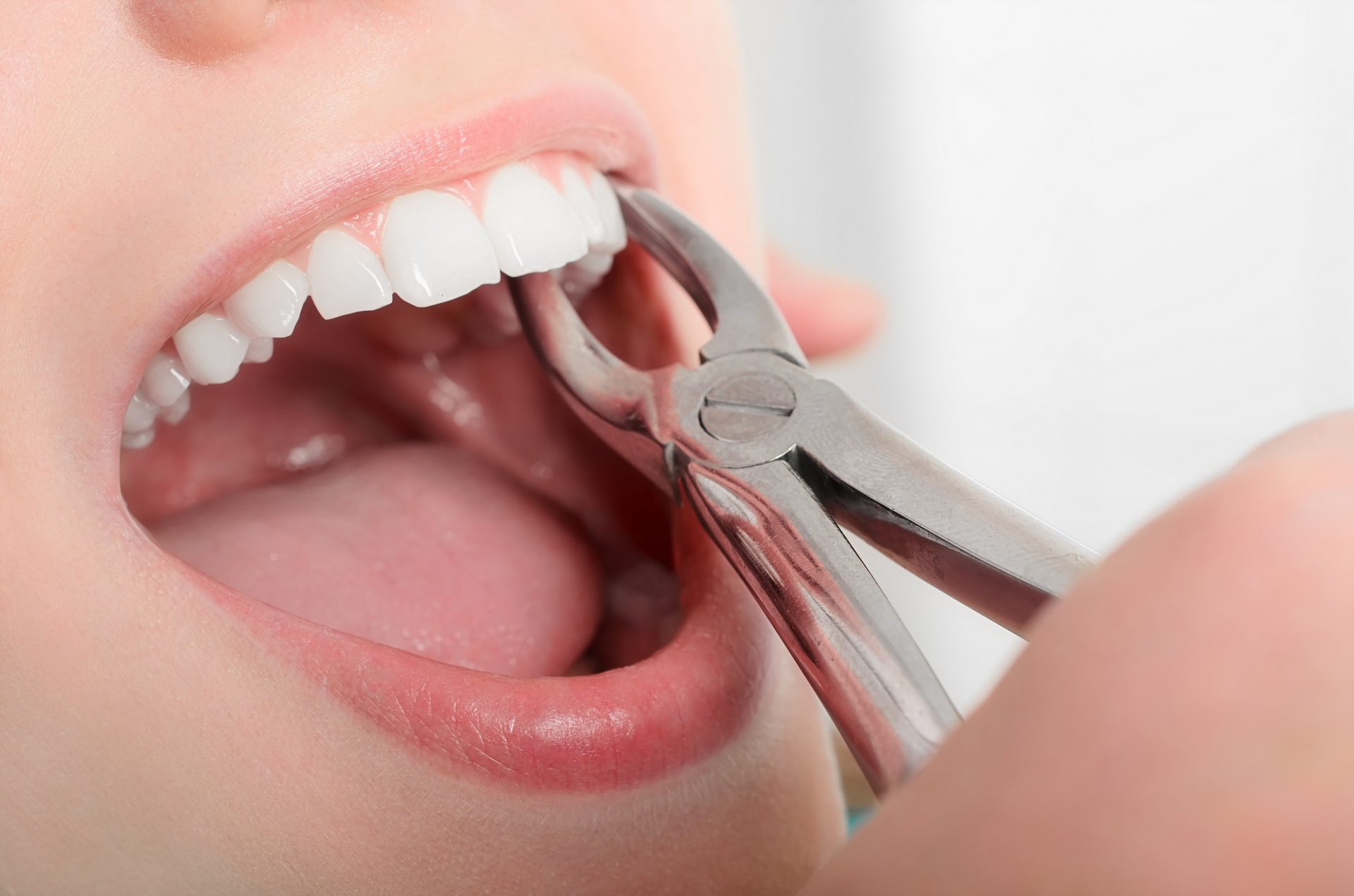

Extraction of tooth
Extraction is performed for positional, structural, or economic reasons. Teeth are often removed because they are impacted. Teeth become impacted when they are prevented from growing into their normal position in the mouth by gum tissue, bone, or other teeth. Impaction is a common reason for the extraction of wisdom teeth. Extraction is the only known method that will prevent further problems. Teeth may also be extracted to make more room in the mouth prior to straightening the remaining teeth (orthodontic treatment), or because they are so badly positioned that straightening is impossible. Extraction may be used to remove teeth that are so badly decayed or broken that they cannot be restored. In addition, patients sometimes choose extraction as a less expensive alternative to filling or placing a crown on a severely decayed tooth.

Pediatric dentistry
Pediatric dentistry is an age-defined specialty that provides both primary and comprehensive preventive and therapeutic oral health care for infants and children through adolescence, including those with special health care needs.